A fuel cell is a device that directly converts chemical energy into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen or a fuel containing hydrogen and oxygen in the air. It is a power generator that produces both electricity and heat simultaneously.
A fuel cell cell is composed of a fuel electrode, an air electrode, and an electrolyte, and a stack is a collection of cells connected in series. A fuel cell power system includes electrical equipment (E-BOP) such as a fuel cell stack that produces electricity, control equipment, and a low-power converter, as well as mechanical equipment (M-BOP) such as an air supply device and a heat exchanger.

Fuel Cell Principle
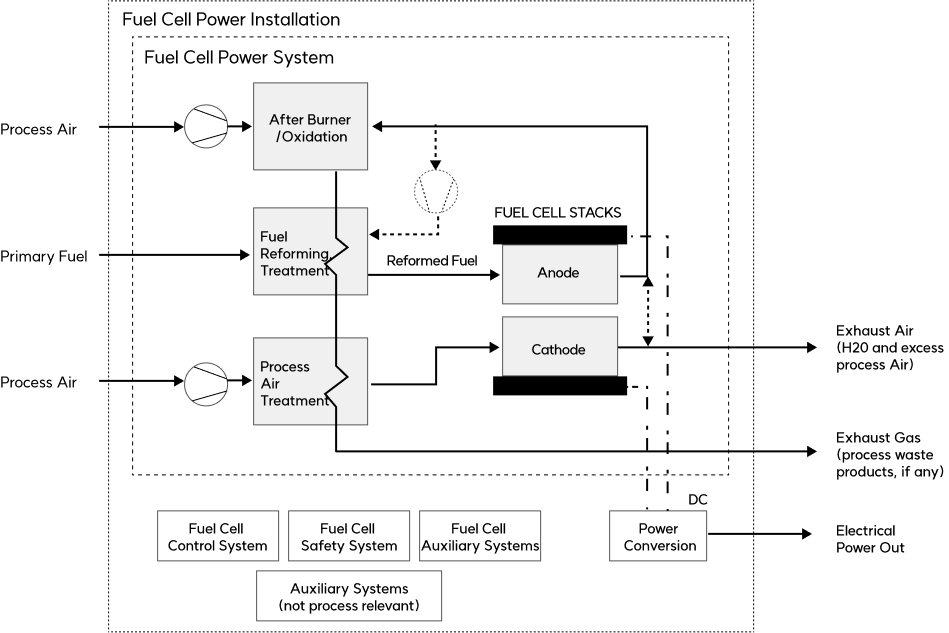
Composition of fuel cell power facility
Fuel cells are power sources that supply electricity by supplying fuel, similar to conventional internal combustion engines. The focus of technological development is on PEMFCs that use hydrogen as fuel and SOFCs that can use various fuels such as diesel, LNG, methanol, and ammonia.
To apply fuel cells to ships, various considerations such as required output, type of ship, operating distance, and installation purpose are necessary, but ensuring safety depending on the type of fuel and installation area is particularly important.
* Separate approval may be required for the reformer if necessary.
Fuel cells for ships are a developing technology, and currently, they are mainly applied to small ships due to the low output caused by technological limitations. However, continuous development of high-capacity fuel cell technology for ships is ongoing.
Korean Register is participating in various research and development activities, from the technology development stage to practical operation of fuel cells for ships, and will provide technical solutions to shipping companies and shipyards based on its expertise.