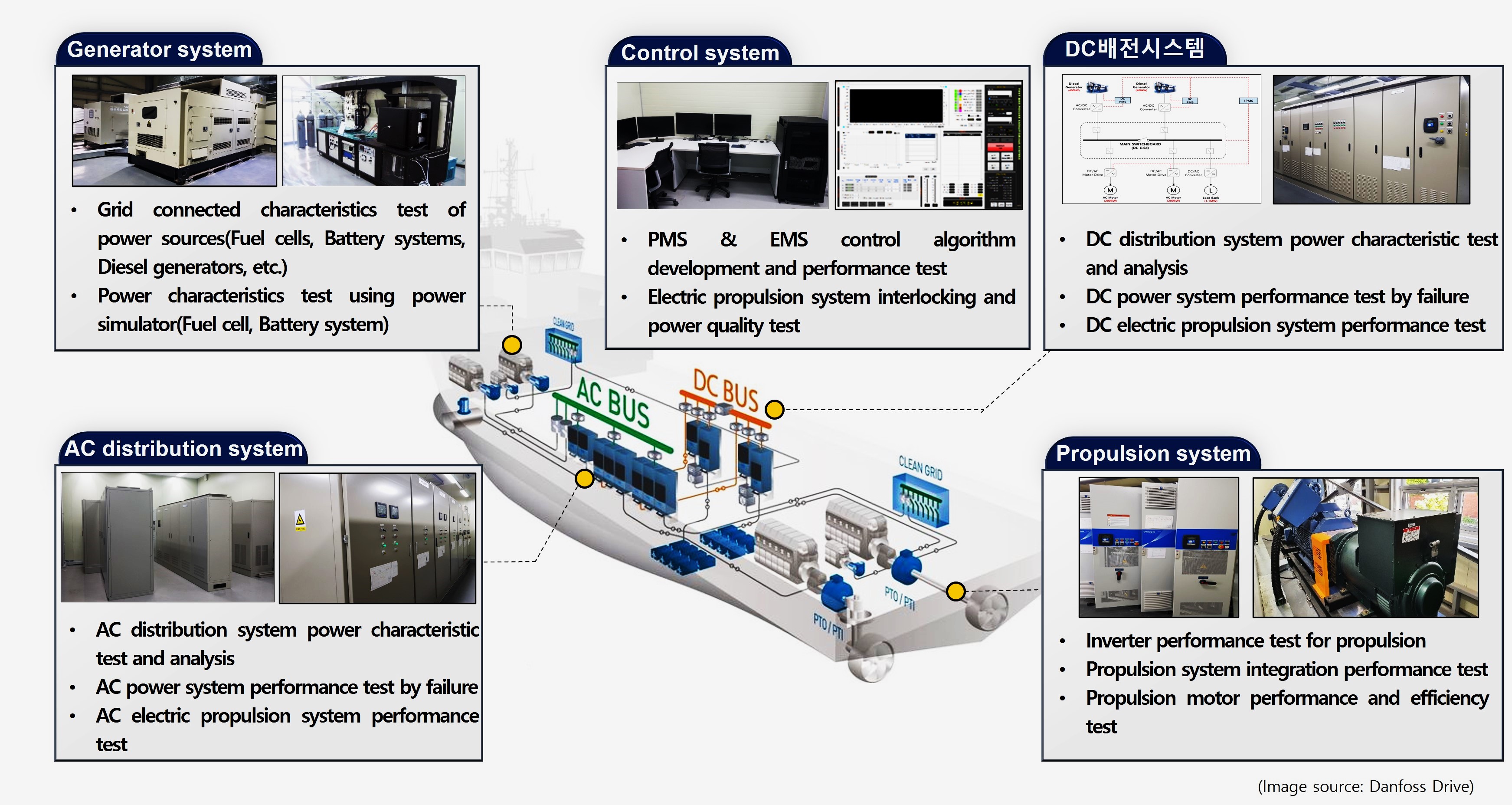
- Definition & Configuration of the Electric Propulsion System
Electric propulsion ships are driven by the electric motor, not the main engine (M/E). They have advantages such as precise speed control and flexible arrangement of equipment, high redundancy, etc. In this regard, it has been mostly applied to offshore service vessels (OSV), LNG carriers, passenger ships, naval vessels, etc. Recently, as the need for eco-friendly coastal ships increases, zero-emission electric propulsion ships equipped with fuel cells or batteries are also getting attention globally. The electric propulsion system is divided into the power generation source, the distribution system that distributes electric power through various power devices, the VFD (Variable Frequency Drive), and the electric propulsion motor.
The power source applied to electric propulsion ships consists of the generator engine (internal combustion engine: diesel, LNG/LPG, methanol, ammonia, etc.), the fuel cell system, the battery system, etc. Fuel cells and battery systems can be used as the main propulsion for small-sized ships with short-distance trips, on the contrary, they can be used as an auxiliary power source for large-sized ships with long-distance trips. The distribution system can be divided into AC distribution (AC-grid) and DC distribution (DC-grid). And the AC distribution method has been traditionally used for a long time and its stability has been verified.
The DC distribution system is a kind of new technology, it can be applied to ships that have DC power (batteries or fuel cells, etc.) or the variable-speed power generation system that can reduce fuel consumption according to the load changes. This DC distribution system is installed by one unit that integrates the distribution system and the power converter, which is called as ‘Distribution & Drive Panel.’ Types of power converters include the general power converters for power supply (AC/DC converters, DC/DC converters, DC/AC converters), and the variable frequency drive (VFD) to drive and control electric propulsion motors. In general, the propulsion motor type is the induction type or the synchronous type.
- Vessel Application Trends
The electric propulsion system is an old technology that has been applied to specific ship types(LNG carrier, cruise ship, passenger ship, drill ship, submarine, offshore service vessels, etc.) for a long time. Recently, in order to respond to the strengthened environmental regulations in the maritime industry, various eco-friendly power sources are being used as main power sources for electric propulsion ships. In particular, DC power sources such as fuel cells and batteries are widely used for DC-grid ships. It is already applied to many battery-driven ships with short-distance. And in the case of fuel cells, various methods have been tried depending on the fuel type, such as LNG and ammonia, as well as hydrogen. As IMO and EU environmental regulations are further strengthened, the demand for electric propulsion ships using eco-friendly power generation sources is expected to increase further. In particular, as the onshore power supply facility (AMP, Alternative Maritime Power) is mandated globally to reduce fine dust in ports, it is expected that onshore power charging of ships using batteries will become more advantageous.